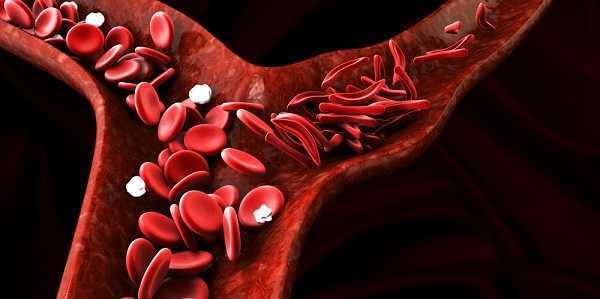
Sickle Cell disease
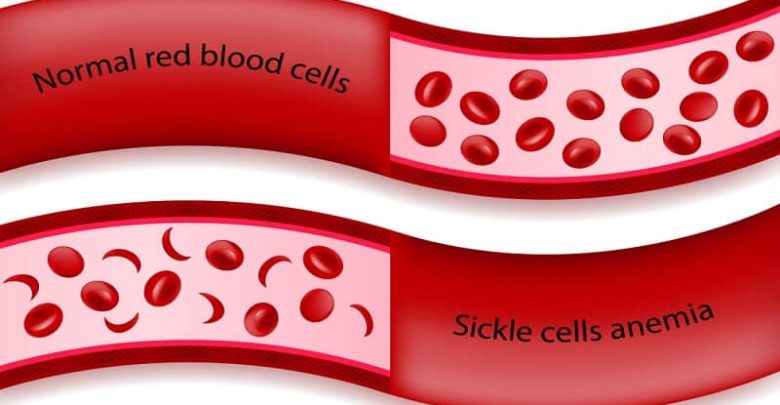
An abnormality of the haemoglobin molecule that alters the shape and stability of red blood cells.
Causes
One of the basic processes of living creatures is to absorb oxygen from the air or from fluids and to transport it to cells where it fuels metabolism. In humans this is achieved by the haemoglobin molecule, carried in millions by each red blood cell. The haemoglobin molecule is like a nest cocooning iron in a special structure, which avidly takes up oxygen but gives it up into the cells. The proteins twist and turn so as to give a particular shape to the molecule, enhancing this function.
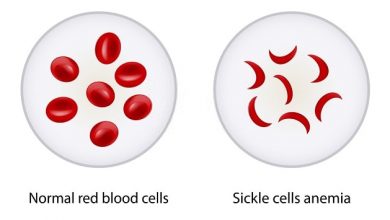
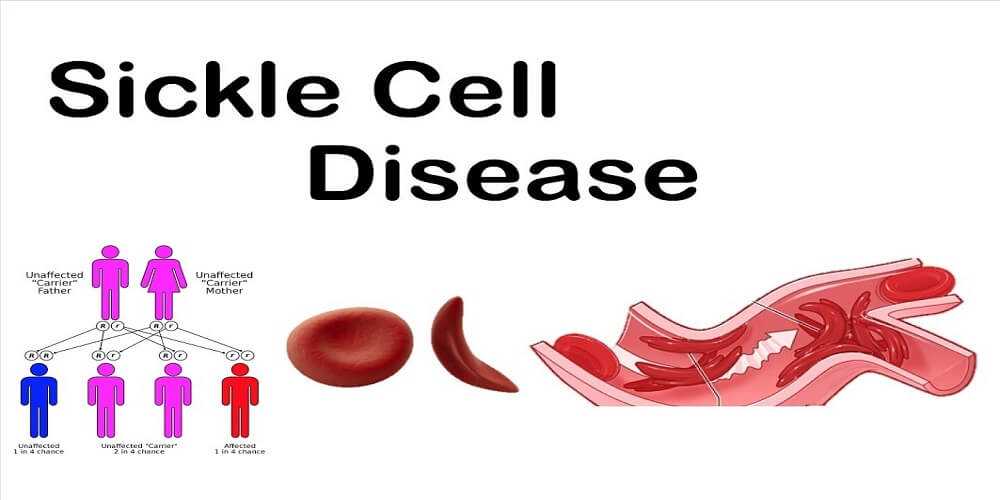
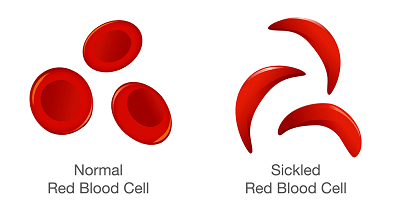
In sickle cell disease, there is an abnormality of haemoglobin caused by a single genetic error that substitutes one amino acid for another. This tiny slip makes the haemoglobin molecule less soluble and the red blood cell more rigid. It loses its bi-concave shape and instead looks curved, hence the term sickle cell.
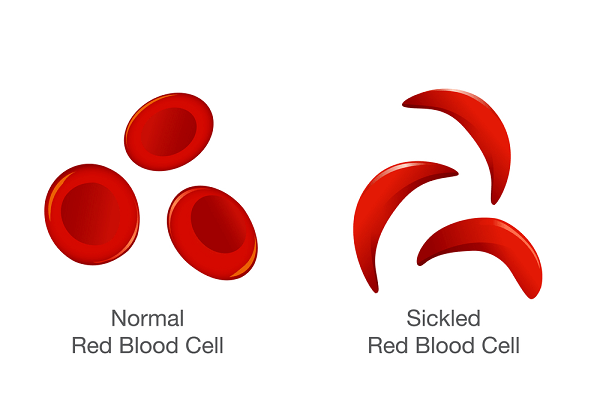
For much of the time the red blood cell gets by, but in certain conditions the abnormal haemoglobin becomes even less soluble and the cells more likely to sickle. These conditions include experience of cold temperatures, infection and lack of oxygen at high altitude.
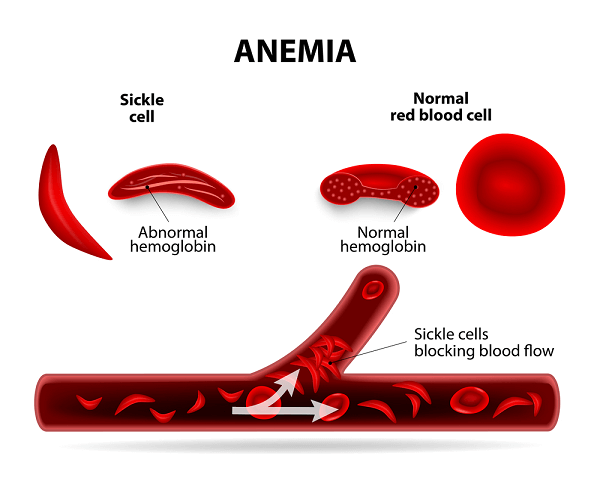
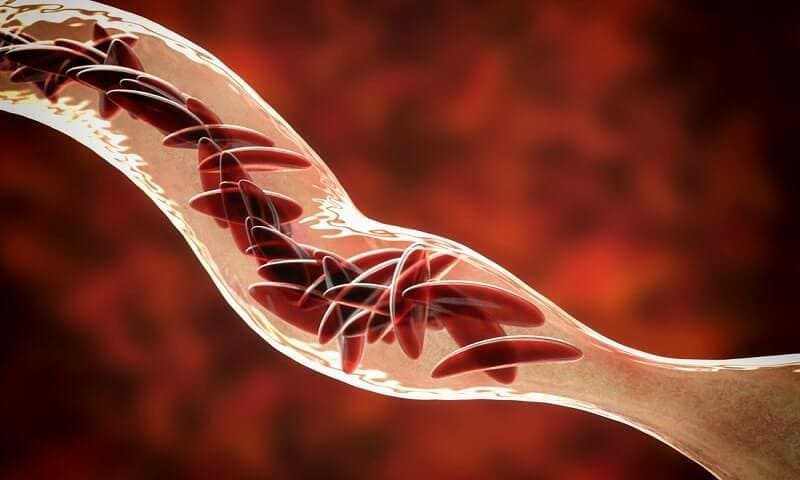
Unlike normal red blood cells, which slip and glide through the narrowest capillaries, rigid sickled cells block small blood vessels and starve surrounding tissues of oxygen. As well as causing pain, this also reduces the life span of red blood cells – normally four months – and causes persistent anaemia.
For reasons not understood sickle cell is extremely common throughout Africa and in populations of African origin, for example Afro-Americans. It is not uncommon in Asians and in the Middle East but is rare in Caucasian populations.

Symptoms
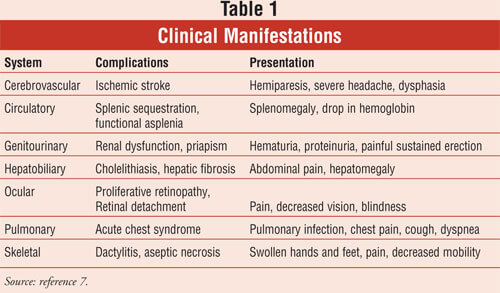
The symptoms of sickle cell disease are mainly the result of blockage of blood vessels – pain that can be anywhere in the body, even abdominal pain. Interference with blood flow in the fingers or long bones can lead to stunted growth and irregularly shaped fingers or toes. The persistent anaemia causes tiredness and increased susceptibility to infection. Eventually there may be kidney and brain damage, too.
The severity of symptoms is highly variable, depending on how much normal haemoglobin the individual also has. Those least affected by the disease have few symptoms except in severe infections or lack of oxygen, whereas those most affected suffer constant pain and anaemia.
Treatment
Many people with sickle cell disease require no treatment and simply need to be aware of the risks that they face. During any surgical procedures it is important for the anaesthetist to give high levels of oxygen via a face mask. Sickle cell disease may be an explanation of otherwise obscure pains.
People suffering sickle cell crises – acute and severe pain due to blockage of blood vessels, usually in the bones or the spleen – need urgent management in a specialized centre to control pain, infection and dehydration from tissue damage.
The anaemia of sickle cell disease cannot be treated in the normal way with iron. Blood transfusion might be necessary in cases of extreme anaemia. Research may, in the future, find a way of getting the body to switch to production of other more benign forms of haemoglobin.
Why is sickle cell so common?
Who is at risk?
Complementary Treatment
No complementary treatment can cure sickle cell disease so do not abandon conventional approaches. I lowever, many therapies do have a role in helping you cope. If you are sensitive to touch, you could benefit from the non-touch techniques of chakra balancing. Yoga and tai chi/clii kung are gentle forms of exercise that can help.